Business Process Automation: What It Is and How It Works
You probably found this page after dealing with repeated work day after day. Maybe an approval got stuck, a contract sat unsigned, or someone asked why their access still wasn't ready.
Those moments add up and eat time you'd rather spend on essential processes.
Business process automation (BPA) takes off that frustration by replacing manual steps with automated workflows that follow rules and move data between your systems.
In this article, you'll learn how business process automation operates, where you can apply it, and how it keeps daily tasks from breaking.
Put structure around the work that keeps falling apart. Use Activepieces to automate it!
TL;DR
- Business process automation uses software to run repeatable work automatically.
- It replaces manual tasks with workflows that follow rules, move data between systems, and finish steps in order.
- Core pieces like triggers, logic, and actions keep work consistent and easy to track.
- Tools like Activepieces connect apps, people, and AI so that complex processes run without constant follow-ups.
What Is Business Process Automation?
Business process automation means software does your tasks in a standardized process. Many teams also call this "business automation" since it covers automation of complex business processes and functions beyond conventional data manipulation and record-keeping activities.
For an automation to begin, it needs an event. Rules then check the details, and actions run in order, such as updating systems or sending messages.
Advanced technologies support this flow by connecting platforms and keeping records visible. Dashboards and logs also show where work pauses, which helps optimize processes so results stay consistent.
With that setup, BPA can be applied to a wide range of tasks, from supply chain management and data entry to employee onboarding and inventory management.
Why Is Business Process Automation Important?
Once you understand how automation works, your next question would probably be: Why and how does it change daily work so much?
- Operational efficiency improves when software handles steps in the right order on its own.
- Automating an entire process end-to-end removes gaps where work often stalls or gets forgotten.
- Automating routine tasks speeds up daily work, in turn avoiding delays that build up during busy weeks.
- Manual errors drop since systems follow the same rules every time and don't rush or guess.
- Cost savings appear when bottlenecks disappear, and end-to-end process automation runs between applications without extra staff.
- Customer satisfaction rises as requests, approvals, and updates move faster.
- Clear tracking helps you better direct your automation effort and allows you to accurately evaluate its effectiveness.
- Data from logs and dashboards supports decision-making and process optimization.
The Building Blocks of Business Process Automation
Business process automation works because a system follows a chain where one step causes the next step to happen without you pushing it forward.
Triggers and Events
Automation starts when something changes, and that change always comes first. That change is the event.
The trigger watches for it and tells the system to begin. Without triggers, nothing moves, even if the workflow looks complete.
Different triggers exist:
- Time-based triggers help with work that must happen on a schedule, such as daily checks or weekly summaries.
- Manual triggers wait for a person to click approve before anything continues.
Then, a condition checks the details before work continues. This step keeps automated tasks limited to the right cases and avoids unnecessary runs.
Once the condition passes, the system passes data to the next step.
Process Logic and Rules
After work starts, logic decides how it should move. Logic gives automated systems a way to react based on data rather than repeating the same step every time.
Some flows move in a straight line. Others branch when values change, such as price, location, or status.
Loops repeat actions for each item in a list, which helps when handling multiple tasks like ordering items. Timing rules let your work pause or run steps at the same time when needed.
After the logic chooses a path, the system follows it consistently.
Decision Points and Conditions
Decision points appear when work should choose a direction. At these moments, the system checks data and picks the next step.
Some decisions lead to "yes" or "no" outcomes. Others route work into several paths.
Approval workflows rely on this setup. A request may move forward on its own until it reaches a level that needs review.
Waiting conditions pause work until something changes, such as a signature or payment. These pauses prevent steps from running too early.
Actions and Outcomes
Actions do the actual work. They update records, send messages, or create files inside connected tools. Systems can run many actions in order without stopping.
Let's say language actions handle text like summaries or replies.
Outcomes show what changed at the end, such as a payment logged or access granted. Tracking failures and retries keeps work from stopping halfway and leaves results behind.
Types of Business Process Automation Software
The following are the common types of BPA solutions:
Robotic Process Automation
Robotic process automation (RPA) operates by copying what a person does on a screen.
You set up a software robot that opens apps, clicks buttons, types values, and moves files the same way you would. A bot can log into a system, copy numbers from your software, paste them into another, then repeat that process all day.
A central system then runs and monitors many bots at once. It even comes in:
- Attended
- Unattended
- Mixed setups
Some tools now handle unstructured data like emails or scanned files, which allows RPA to support more complex tasks such as report generation, though changes in screens can still cause issues.
Business Process Management
Business process management (BPM) focuses on how work moves from start to finish rather than how clicks happen.
You can use it to define a task automation process tied to business functions that include people, rules, and systems working together.
It often starts by designing the current flow, then modeling an improved version. Once live, the system routes tasks to people or tools, tracks progress, and records timing.
Human review is still part of the process, especially for decisions that software shouldn't make alone.
Workflow Automation
Workflow automation connects steps between people and platforms to automate repeatable organizational processes.
Typically, this is how it works:
- A trigger starts the flow
- Rules guide decisions
- Actions move work forward
Your tasks follow the same path each time, which reduces confusion as volume grows.
Digital Process Automation
Digital process automation focuses on automating repetitive tasks while supporting larger automation strategies tied to digital transformation. It connects user-facing forms with back-end systems, so workflows.
Information enters through portals or apps, systems handle processing, and updates keep users informed as work continues. Such a setup helps you streamline operations and keep customer and employee experiences simple.
How Activepieces Supports End-to-End Business Process Automation
Activepieces is an open-source automation platform that connects apps, people, and AI agents.
Core features that make this possible:
- Visual workflow builder that shows the entire flow of work step by step, so anyone can see how a process runs.
- Simple setup that lets you create automation solutions with minimal coding knowledge, while still allowing deeper customization when needed.
- Built-in AI support so automated processes and AI agents can remember past interactions and use that context in later steps.
- Integration library (of 597 pieces) that connects existing systems like finance tools, support platforms, developer tools, HR, customer relationship management (CRM) software, and more.
- Human approval steps that pause workflows until someone reviews or confirms an action.
- Secure deployment options, including self-hosting, for teams that need full control over data.
- Clear logs and run history so you can see how automation behaves in business operations.
Connect tools, AI agents, and human approvals in one workflow. Start with Activepieces!
Common BPA Examples in Activepieces
These are the manual processes and complex tasks in your business that you can automate in Activepieces:
Client Onboarding
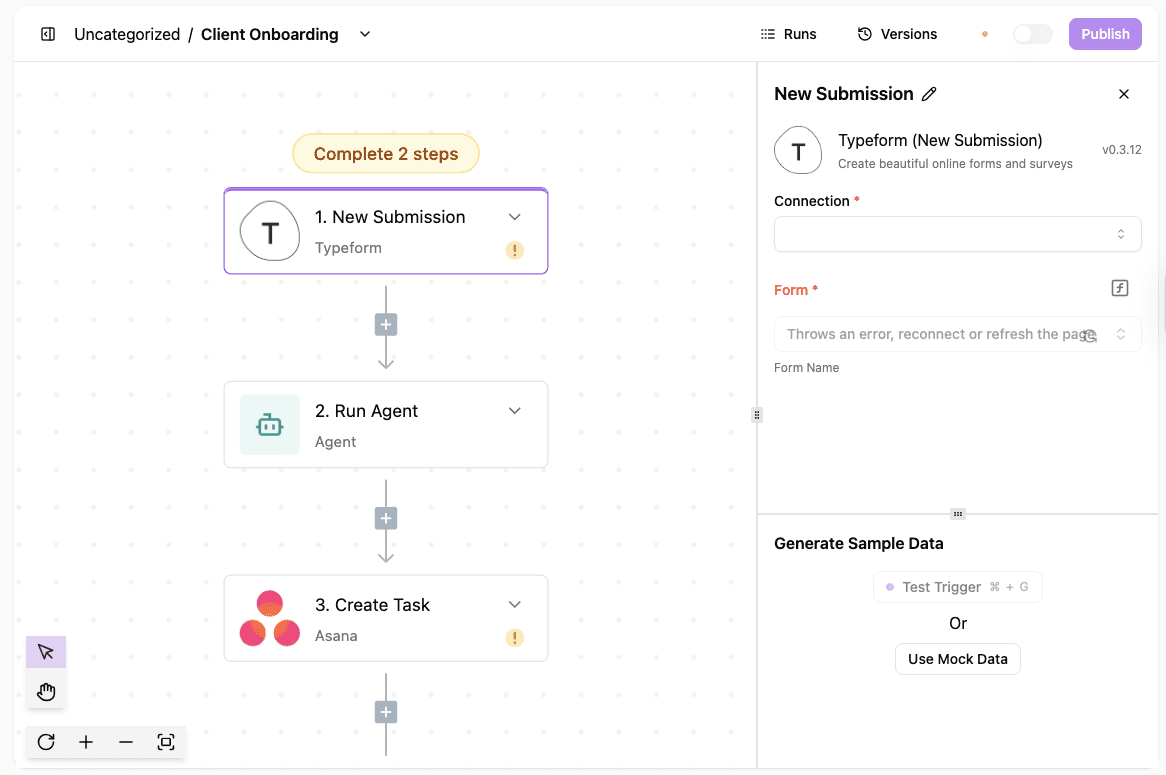
Client onboarding in Activepieces starts when a form is submitted and continues without breaks or manual handoffs.
The same structure works for employee onboarding, which means you can reuse the flow for any onboarding process with small edits that match your own processes.
What happens in the workflow:
- A form trigger captures new client details as soon as they submit
- An email action sends a welcome message with the next steps
- A CRM step creates the client record automatically
- Task creation assigns follow-ups to the right people
- A Slack message alerts the team that onboarding has started
This setup removes back-and-forth emails and cuts down administrative tasks tied to setup work.
Get the template here: Client Onboarding
Customer Support Ticketing
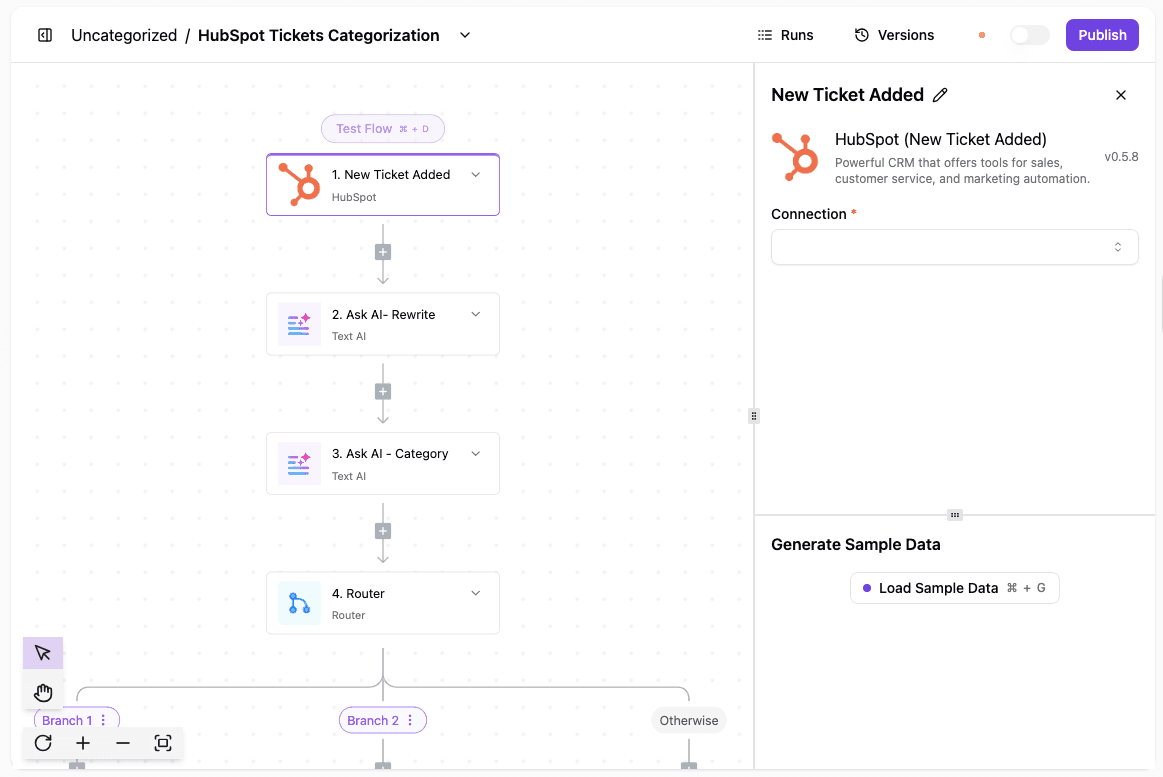
Support requests move faster when routing happens right away. Activepieces watches for new tickets and handles sorting before a human ever opens the message.
How the ticket flow works:
- A trigger detects a new ticket in HubSpot
- AI rewrites the description so it reads clearly
- AI assigns a category based on the request
- Routing sends the ticket to the correct team
- Slack notifications alert the team instantly
Sorting happens automatically, which keeps requests from sitting in the wrong queue.
Get the template here: Customer Support Ticketing
Invoice Reminder
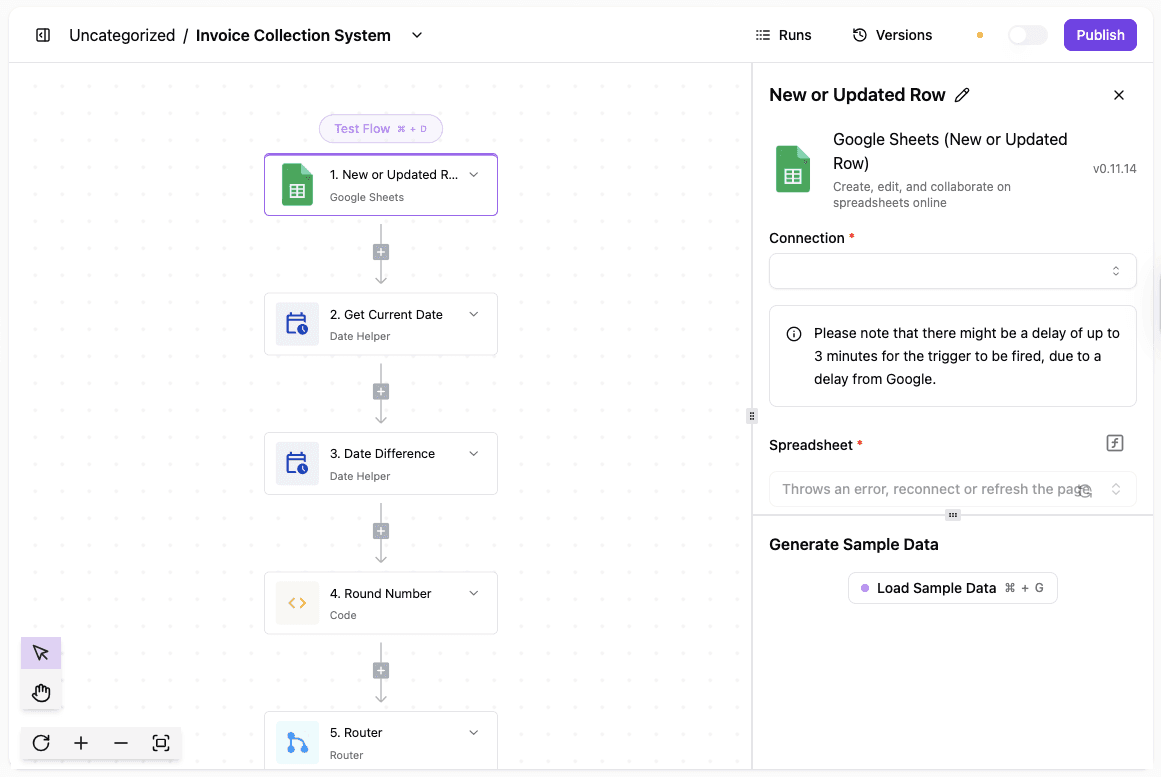
Invoice processing often stalls when reminders depend on memory. Activepieces tracks overdue payments and handles follow-ups based on timing rules.
Steps inside the reminder flow:
- Payment data gets pulled from a source like Stripe or Sheets
- The system calculates how long each invoice is overdue
- Messages go out based on the delay length
- Records update once payment arrives
Get the template here: Invoice Collection System
Run AI-Assisted Business Process Automation Using Activepieces
Activepieces supports intelligent automation by letting AI take part in workflows rather than acting as a separate add-on.
AI agents inside Activepieces can read messages, understand intent, and act based on past context, which makes it possible to automate complex workflows that don't follow strict rules.
A single flow can move data through multiple systems, such as forms, databases, chat tools, and internal apps. Context stays available, so the system reacts consistently when similar requests appear again.
Besides that, human approval is available when judgment is needed, while routine steps run on their own.
All of these let your teams streamline tasks that normally require constant switching between tools and follow-ups.
Keep AI, approvals, and systems in one automation layer. Explore Activepieces now!
FAQs About Business Process Automation
What is business process automation?
Business process automation means using software to run repeatable work without manual handling.
BPA is the use of software to automate repeatable, multistep business transactions such as approvals, updates, and handoffs, using automated workflows to support core processes.
What are the five stages of BPM?
The five stages are mapping the current process, designing improvements, running the process, monitoring results, and adjusting steps to improve efficiency over time.
What is AI automation of business processes?
AI automation adds analysis to automation.
Intelligent process automation uses AI and machine learning to analyze data, apply natural language processing, and guide workflow orchestration when fixed rules are not enough, using modern automation technologies.
What is the difference between RPA and BPA?
RPA copies user actions on screens, while BPA manages full processes. RPA handles tasks, while BPA coordinates systems, logic, and decisions end-to-end.


