Workflow Automation: How It Works + Benefits

Working hours are daily lost to data entry, approvals, follow-ups, and other redundant tasks that never stop. Manual processes push responsibility onto your attention, forcing checks, reminders, and copied details between tools.
Workflow automation refers to software that carries your work forward. You need this because automated processes remove manual work, reduce human error, and give you control back.
This article explains how workflow process automation works and what problems it solves in your business operations.
TL;DR
- Workflow automation uses software to move work forward automatically.
- Benefits include faster execution, fewer errors, and more time for meaningful tasks for business users.
- Common tools include no-code platforms, integration software, and AI-driven automation tools.
- Automate work by spotting repeated time drains, mapping each step clearly, starting with simple flows, then choosing tools that match how your team builds.
- To get started, identify repetitive high-impact tasks, map the process, automate a simple flow first, and choose a platform that fits your scale, control, and security needs.
What Is Workflow Automation?
Workflow automation is the use of software to handle repetitive tasks in your business operations. Automation has quickly shifted from simple “if this, then that” rules to something closer to a digital nervous system within companies.
Early systems followed strict paths. One rule fired, one action followed. Software connects steps, decisions, and data so your work moves forward automatically.
For example, when a new hire is marked as “Hired,” the system automatically sends their contract for e-signature, alerts IT to prepare a laptop, and schedules first-week training.
Those flows rely on triggers, logic, and actions working together. That setup makes it easier to identify repetitive tasks and automate them before delays appear.
How Workflow Automation Works
Once work enters your system, software takes responsibility for moving it forward. Each step connects to the next through rules, so progress continues even when no one watches.
1. Triggers Start the Workflow
Every automated workflow begins with a trigger, which works as the spark or inciting event that tells your software, “Wake up, something happened, and you need to act now.”
Without that signal, instructions stay idle. Triggers watch sources like customer relationship management (CRM) platforms, websites, or spreadsheets for change. When a change appears, your workflow automation system reacts and passes data forward.
Your automation platform can also check for a trigger in the source app every few minutes.
Different events start different flows. Time rules handle repeating tasks, while user actions respond to clicks or uploads.
2. Steps, Actions, and Data Flow
After the trigger fires, the steps guide movement. Each step represents progress, which helps your software coordinate work.
Some tasks can happen in a specific order, such as:
- Step 1: Save the invoice
- Step 2: Notify the finance team
Actions perform the work: Messages are sent, records are updated, files are generated, and AI reviews text.
Data moves as a single package with each step. Often, data needs to change format as it flows.
A workflow can further take a “Raw Date” from a form and transform it into a “Standardized Format” before saving it to a finance system.
3. Logic Conditions and Decisions
As data moves forward, logic decides direction.
For instance, “Only continue if the order is over $1,000” blocks work that doesn’t meet that threshold. This setup allows one single workflow to handle multiple types of situations, such as handling a $10 refund differently from a $10,000 refund.
Each decision checks specific values. Your automated system looks at the data it has collected and compares it against rules.
When the result is “True,” the workflow goes down “Path A.” If it’s “False,” it goes down “Path B.” More complex cases are split further, such as routing a support ticket to:
- Billing
- Technical support
- Sales
- Returns
4. Orchestration Error Handling and State
As flows grow, coordination becomes necessary. Orchestration manages how steps depend on one another, so one action waits until another finishes, even when systems differ.
When problems appear, error rules take over. Retries attempt tasks again, fallback paths switch tools, and rollbacks undo partial changes.
The state keeps memory during all of this. State management keeps track of variables like “Who is the current logged-in user?” or “What items are in this specific shopping cart right now?”
That memory allows work to continue from the correct point.
Benefits of Workflow Automation
Once you implement workflow automation, you’ll experience these benefits:
Increased Productivity
According to Harvard, every time you stop a creative task to copy an invoice into a spreadsheet, it takes your brain an average of 23 minutes to regain deep focus.
Automating individual tasks removes those interruptions by letting software handle repetitive work in the background. One single trigger, like a customer signing a contract, can launch 50 different actions simultaneously.
This shift creates more efficient workflows and frees up space for more important work. Faster responses also help speed up agent response times and increase customer satisfaction.
Standardized Execution
When you rely on humans to follow a manual checklist, they inevitably skip steps, take shortcuts, or interpret instructions differently. Routine tasks drift as volume grows.
Automation locks steps into a fixed path so every request follows the same rules. Efficient business processes form when logic stays the same each time.
Besides that, the process cycle time shortens because approvals and handoffs no longer loop back for fixes.
Easier Tracking and Reporting
Since every step is automated, your system can create a digital timestamp for every action.
If an auditor asks, “Did you verify this customer’s ID?” you don’t search emails. You show a standardized log proving the check ran every time.
You can also receive automated notifications and alerts of any pending approvals or reviews before delays grow. Assigning tasks through software removes confusion.
Manual data entry drops, while reporting improves. You can see your cycle time change in real time, which improves process key performance indicators (KPIs) and performance metrics without manual reports.
Faster Decision-Making
Decision-making is often slow because of noise. You have 500 emails, but only five require a high-level decision.
Automation filters routine approvals, which enables businesses to focus on essential tasks. Manual processes shrink as systems apply rules instantly.
Common Workflow Automation Tools
These are the common workflow automation solutions:
No-Code Platforms
As work grows more complex, you need to look for ways to improve workflow management without turning every request into a development ticket.
No-code tools answer that need by letting you build flows through visual steps. You drag actions onto a canvas, connect them, and then decide what happens next.
You can use no-code software for recurring tasks, such as moving form entries, routing requests, or sending updates. It simplifies the automation process and gives non-technical users control over daily work, too.
Low-Code Workflow Automation Software
Low-code platforms offer a visual interface but also allow small pieces of code when logic requires extra precision.
A standard block may not handle a complex calculation or custom connection. In that case, a short JavaScript or Python snippet fills the gap.
Even then, you don’t need to write code from scratch. You can type something like “Write a script that takes this messy date format and turns it into ISO 8601,” and the AI generates the code for you.
Integration Platforms
As more tools enter a company, business automation often breaks down due to data silos. Integration platforms fix that by translating data as it moves.
These platforms focus on replacing manual tasks that once held your teams back. You simply tell the platform “Sync my ERP and my CRM,” and the AI identifies matching fields, builds security rules, and tests the connection.
That process creates seamless integration without forcing you to rebuild existing systems or change how you work.
Robotic Process Automation and Task Automation Tools
Some work still depends on older software with no connections available. Robotic process automation software uses “bots” to perform tasks that a person would do on a screen. These bots can click buttons, type values, and move files just like a user would.
On the other hand, task management tools can run simple actions on a device to handle repeat steps, such as sorting files or filling forms.
Both approaches reduce effort by shifting repetitive work away from people and into software.
How to Automate Your Business Workflows
To automate your workflows, you need to:
Identify Repetitive High-Impact Processes
Start by paying attention to actions that repeat throughout the day. Some tasks happen so often that they fade into the background, even though they consume hours over time.
Moving a lead from an email into a spreadsheet can take two minutes, yet doing that 30 times a day adds up to roughly 260 hours a year. Whenever data is moved by hand from one system to another, software can handle it faster and more reliably.
Some of the usual workflow automation examples include:
- Filing expense reports
- Updating deal stages in the sales process
- Asking marketing team members to share numbers
- Managing paid campaigns all fall into this group
Automation can delegate tasks and remove those slow points.
Map Your Workflow Before Automating
After choosing a process, write down how it works today, step by step. Start where the work begins and follow it until nothing else needs to happen. Include decisions, approvals, and pauses.
Separating steps that require human review from those that don’t simplifies the flow before software enters. Cleaning up confusion early prevents broken automation later and helps streamline processes in a controlled way.
Start Simple Then Expand
Begin with a narrow focus so results stay predictable. One trigger connected to one action provides a clear test. Let it run for a short period and watch what happens.
Once the basic flow runs without issues, automate tasks like routing messages or applying conditions. Adding logic is most effective after the foundation proves stable. Building in layers keeps troubleshooting manageable and avoids fragile setups that break under small changes.
Each new step should solve a problem and fit naturally into the existing flow rather than forcing everything into one large setup.
Choose the Right Workflow Automation Platform
The right platform depends on who builds and maintains workflows over time.
Business users often need visual tools that show steps clearly and reduce setup friction. Technical teams may prefer deeper control, custom logic, or self-hosting options.
Some platforms charge per action, which grows expensive as usage increases. Others support higher volume without steep jumps. Data handling also deserves attention.
Sensitive information may require tighter control over where data moves and who accesses it, too.
Upgrade Your AI Workflow Automation With Activepieces
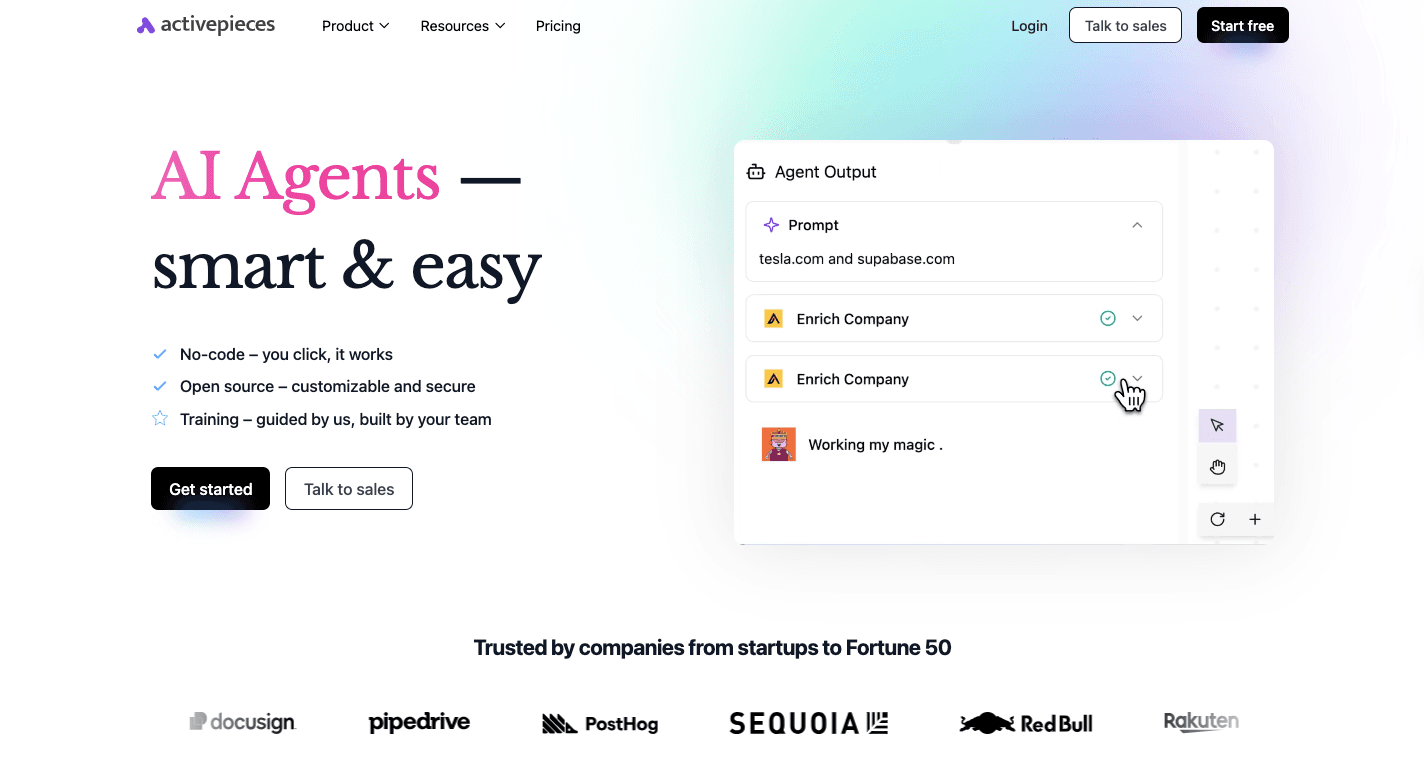
Finding the right workflow automation software means knowing how work moves and who controls it.
Activepieces is an AI automation platform that helps when flows grow beyond simple actions and turn into complex workflows that involve reviews, approvals, and follow-ups.
It supports automation through a set of features, such as:
- A vertical canvas shows each step in order, which helps you follow logic when handling multiple tasks inside one flow.
- Activepieces connects with email, CRMs, spreadsheets, and collaboration tools, so updates move between apps without copying.
- Support for existing systems removes the need to replace software your team already uses.
- Self-hosting and permission controls provide robust security measures when data needs protection.
- One trigger can manage updates, notifications, and approvals, which helps automate entire processes without losing visibility.
Sign up for free or contact sales to learn how the platform works!
FAQs About Workflow Automation
What is workflow automation?
Workflow automation describes using software to move work from one step to the next. It replaces repetitive coordination with rules so customer interactions, approvals, and updates happen automatically.
You spend less time pushing work forward and more time optimizing resources for more productive tasks.
Which tool is used for workflow automation?
The right workflow automation tool depends on how much control, scale, and flexibility you need. Platforms like Activepieces handle everything from simple routing to complex tasks while helping business teams streamline workflows without relying on constant technical support.
What are the three types of workflows?
Workflows usually fall into three groups:
- Sequential workflows move work through steps.
- Parallel workflows run several actions at the same time.
- Conditional workflows change direction based on rules or data.
What are the key features of workflow automation software?
Workflow automation software includes visual builders, integrations, logic rules, approvals, and monitoring so you can manage work without guessing what happens next.
What is the difference between workflow automation and business process automation?
Workflow automation focuses on individual flows or tasks, while business process automation connects multiple workflows into larger end-to-end systems that span departments and tools.


