8 Data Integration Tools: Key Features, Benefits & Top Picks
Data flows nonstop in every business. Some of it comes from: customer sign-ups, sales platforms, and day-to-day operations. When each system keeps its own version, the odds of numbers not matching are higher.
Data integration solutions fix that and link sources into a single view. You get faster reports, fewer manual edits, and cleaner inputs that improve data quality. Other platforms even push updates the moment they happen, so you get real-time data integration for dashboards and alerts.
In this article, you’ll learn about the top data integration tools and which options fit different needs.
TL;DR
- These are the best data integration tools:
- Activepieces
- Matillion
- Airbyte
- Oracle Data Integrator
- Fivetran
- SAP Data Services
- Informatica
- Qlik Talend
What Is Data Integration?
Data integration brings information together so you can actually use it. In practice, it’s the process for combining data from various sources into a single setup that supports precise reporting and planning.
The stages follow a typical process:
- Pull records from source systems
- Run data preparation to fix errors and line up formats
- Do data transformation to shape values into something consistent
- Transfer data into a data warehouse or data lake
- Keep it up to date with either batches or nonstop data ingestion
Different methods cover different needs of large and complex data integration requirements. The extract, transform, load (ETL) process handles cleaning before loading, while extract, load, transform (ELT) processes rely on cloud systems to process raw records. APIs link apps for direct sync, and streaming allows instant updates.
All of it matters not only for reporting but also for future work, since machine learning depends on large, reliable datasets.
Benefits of Using Data Integration Tools
When data stays locked in data silos, your reports turn messy. Connecting everything through robust data integration gives you a single, trusted view. You don’t waste hours second-guessing numbers because the information already lines up.
Day-to-day work gets easier, too. Automated flows cut down on mistakes that come from manual data entry, and you can spend more time on real data operations. Integration also raises the quality of data management since records move in consistent formats and errors get flagged early.
You can pull in unstructured data too, such as emails or logs, and combine it with structured records for deeper insights. Data migration tools move data between computers, storage systems, or application formats, so old systems can shift into modern platforms without losing history.
With everything in place, you cut costs, meet compliance needs, and keep your data ready for whatever comes next.
Types of Data Integration Software
Modern data integration tools vary by method and setup, and each fits different needs. Common categories include:
- ETL tools - Handle data extraction, clean records, and finish by loading data into a warehouse.
- ELT tools - Move raw records directly into cloud-based data warehouses, using the warehouse itself for heavy processing.
- Replication tools - Manage constant data movement between systems, which helps with backups and disaster recovery.
- Virtualization tools - Create a single view without moving the information physically.
- Streaming tools - Process events as they arrive, which is useful for IoT or real-time analytics.
- Change data capture (CDC) tools - Track inserts, updates, and deletes to keep systems aligned.
Some setups extend further. Enterprise data fabric combines multiple methods to manage complex projects. Deployment also varies, from on-premises systems that provide control to open-source frameworks that give direct control over data structures to cloud services that scale quickly.
8 Best Data Integration Tools in 2026
Selecting the right data integration tool means looking beyond features: robust customer support, metadata management, and a data catalog for the organization. The tools below will lead in 2026 in making integration faster.
1. Activepieces
Activepieces is an open-source automation tool that eliminates the need for manual data entry. It connects apps through flows, which link triggers and actions across different services.
Inside Activepieces, there are 510+ data integrations called pieces that you can connect to. That includes CRMs, finance tools, project managers, and AI services. Marketing data is easy to route through flows, so your reports stay current, and campaigns stay consistent.
The intuitive user interface lets anyone build automations without technical expertise or extensive coding knowledge. Developers still have the freedom to create custom pieces through its TypeScript-based framework.
For enterprises, the option to self-host Activepieces means tighter control over data security. Teams in regulated industries prefer that setup. The cloud edition offers predictable flat-rate pricing for unlimited tasks, which helps you scale without cost surprises.
Key Features
- No-code builder - Drag-and-drop interface to create flows without writing code.
- Pre-built pieces - Hundreds of connectors for apps like Google Sheets, HubSpot, Stripe, and Slack.
- Custom pieces - Developers can extend the platform with TypeScript to build new integrations.
- AI integration - Native support for AI agents that can analyze, summarize, or generate content in workflows.
- Self-hosting - Full control over data through on-premise deployment.
- Open ecosystem - Community-driven library of pieces on npm with ongoing contributions.
- AI Copilot - Assists users inside the builder in designing flows faster.
- Security controls - Role-based access, audit logs, and the ability to run in isolated environments.
Integrations

Activepieces offers a growing library of integrations, referred to as pieces. As of now, the number sits at 510 pre-built connectors, but the count continues to rise since the community contributes new ones regularly.
Some of the pieces you could use:
- OpenAI
- ElevenLabs
- HubSpot
- Google Sheets
- Microsoft Excel 365
- Slack
- Discord
- WooCommerce
- ClickUp
- ActiveCampaign
- Microsoft Dynamics CRM
- Zoho Invoice
The open-source framework means developers can also create custom pieces, so the library expands beyond what’s officially listed.
Pricing
For the Standard plan, it’s free to start, then $5 per active flow per month. You get ten free active flows, unlimited runs, AI agents, unlimited MCP servers, unlimited tables, and email support.
Ultimate is annual and quote-based. It adds enterprise controls like security and governance, access controls, custom RBAC, SSO, audit logs, centralized AI billing, management APIs, Git sync, private pieces, and dedicated support. You can run it in the cloud or on-prem.
Activepieces Embed is annual as well, starting at $30k a year. It lets you embed the builder and AI agents into your own product with a JavaScript SDK, custom branding, private features, and dedicated support.
The free Community Edition is open-source and self-hosted, with no limits on tasks, but requires managing your own server.
2. Matillion
Matillion runs as a cloud-based integration platform that relies on ELT. Data from multiple sources goes straight into warehouses like Snowflake, BigQuery, Redshift, or Databricks, and the process happens inside those systems.
Analysts can just drag and drop steps when designing flows inside Matillion, while engineers can write SQL or Python when they need deeper control. For organizations with complex data workflows, it adds scheduling, automation, and monitoring.
It further shapes records into accurate data for reporting and AI projects. Acting as a data quality tool, it checks formats, maps values, and resolves errors before you run analysis.
Compliance features also help with data governance, offering role-based access, audit logs, and version control. Together, these functions let you keep quality and security in focus.
Key Features
- Data connectivity - Links to hundreds of databases, SaaS tools, APIs, and files. Custom connectors extend coverage further.
- Change data capture - Tracks inserts, updates, and deletes in real time to keep downstream systems aligned.
- Data transformation - Offers a visual ELT builder for simple use and scripting for engineers.
- AI and machine learning - Includes Maia for natural language pipeline design and support for unstructured inputs.
- Pipeline orchestration - Handles scheduling, automation, and monitoring with lineage tracking.
- Security and governance - Provides audit logs, version control, and access control for enterprise compliance.
Pros
- Visual builder helps non-technical users
- Connects with cloud warehouses like Snowflake and BigQuery
- AI assistant for building and optimizing pipelines
- Central hub for orchestration and monitoring
Cons
- Less flexible for code-heavy projects
- Features differ across supported warehouses
- Platform instability reported by some teams
- Support response is sometimes slow
Pricing
Matillion pricing isn’t publicly posted.
3. Airbyte
Airbyte is an open-source platform that supports structured and unstructured data without locking you into a single vendor.
It follows the ELT model, so records come out of data sources like SaaS apps, APIs, or databases and land directly in a data warehouse or data lakes. Processing then happens inside the destination system, which saves time and scales better than older methods.
You have the option to host it yourself for full control. Either way, you can pick a managed cloud version or set up a hybrid that mixes both.
Since it’s open-source, developers can build new connectors when needed. That makes Airbyte a fit for teams that need to integrate data from many systems while still keeping costs under control.
The connector library is large and active, with community members adding new options often. For anyone looking to consolidate their data in their data warehouses, data lakes, and databases, Airbyte covers a wide range of use cases while leaving room for customization.
Key Features
- Connector library - Over 600 pre-built connectors for APIs, databases, files, and apps.
- Custom connectors - Toolkits let developers design their own when pre-built options fall short.
- Flexible deployment - Can be self-hosted, cloud-managed, or set up as a hybrid.
- Change data capture - Tracks inserts, updates, and deletes for efficient sync.
- ELT and ETL support - ELT is the default, but ETL is possible when transformations need to happen first.
- Integration with modern stacks - Works with dbt for transformations and with Airflow or Dagster for orchestration.
- Enterprise security - Paid versions include audit logs, access controls, and single sign-on.
Pros
- Large and growing connector library
- Open-source with customization options
- Near real-time sync with change data capture
- AI-ready for structured and unstructured inputs
Cons
- Self-hosted setups need technical skill
- Resource-heavy to keep running smoothly
- The user interface is less polished than some tools
- Open-source support depends on community help
Pricing
Airbyte pricing isn’t publicly posted.
4. Oracle Data Integrator
Oracle Data Integrator (ODI) moves information using an ELT approach. Data comes from source systems and lands in the target database. Once there, the database itself runs the data processes and handles the transformations without an external server.
The platform is often used in complex data environments where you need both speed and precision. Developers can build mappings that describe the flow of information from source to target.
Reusable components, called knowledge modules, supply the code patterns needed for loading, transforming, and checking records. These pieces make large projects more consistent and easier to maintain.
ODI connects with a wide set of technologies as well, so you can bring all the data together for reporting or analytics. It supports seamless integration to traditional relational databases, modern cloud platforms, and big data tools like Hadoop and Spark.
Key Features
- ELT architecture - Pushes transformation logic into the target database for faster and more efficient execution.
- Knowledge modules - Provide pre-built, reusable templates for common integration tasks while allowing customization.
- Broad connectivity - Links to databases, cloud services, SaaS applications, and big data platforms.
- Change data capture - Captures inserts, updates, and deletes in real time to keep systems aligned.
- Declarative design - Developers describe the integration flow, and ODI generates the required code automatically.
- Orchestration and monitoring - Includes scheduling, job management, and error tracking within the platform.
- Metadata-driven governance - Tracks lineage, supports compliance, and offers clear reporting for audits.
Pros
- Handles large datasets efficiently with ELT
- Reduces hardware costs by using the target database’s resources
- Connects with a wide range of systems
- Real-time updates with change data capture
Cons
- Steep learning curve for new users
- Relies on the target database’s performance
- Interface feels dated compared to modern tools
- Initial load can put pressure on resources
Pricing
ODI pricing follows Oracle Cloud’s usage model. Workspace Usage costs $0.16 per hour. Data Processed is charged at $0.04 per gigabyte per hour.
Pipeline Operator Execution is billed at $0.30 per hour. Larger enterprises often negotiate custom rates based on workload and contract size.
5. Fivetran
Fivetran is a managed enterprise data integration platform that moves information from many applications and databases into a central location without much manual work.
It automates the steps needed to build a pipeline, so you don’t spend hours writing code. The system connects to hundreds of sources, pulls records out, and keeps them up to date with little effort from engineers.
Other than that, it automates data pipeline setup and takes care of changes that often break pipelines, like new columns or renamed fields. Through an automated hands-off approach, it does data mapping to reduce errors and help maintain data accuracy over time.
That makes it possible for your analysts and engineers to spend less time fixing sync problems and more time working with the information itself. Centralizing records into cloud data warehouses and lakes supports analytics, reporting, and AI use cases, too.
Key Features
- Pre-built connectors - Over 740 fully managed connectors for databases, SaaS apps, and event streams.
- Automated sync - Continuously pulls data from sources and updates destinations on a schedule.
- Change data capture - Detects inserts, updates, and deletes for efficient incremental updates.
- Schema management - Adjusts automatically when fields are added or renamed.
- Historical syncs - Loads complete history on first setup and supports free re-syncs when needed.
- dbt integration - Works with dbt for transformations once the data is in the warehouse.
- Security and compliance - Encryption at rest and in transit, SOC 2, GDPR, and HIPAA compliance.
- Monitoring and logs - Provides metadata and sync activity logs for auditing.
Pros
- Easy to set up, even for non-technical users
- Automates updates and schema changes
- Large set of stable connectors
- Reliable incremental updates keep data fresh
Cons
- Costs rise quickly with large or fast-changing datasets
- Limited flexibility compared to custom pipelines
- Troubleshooting requires reliance on support
- Lacks built-in dashboards or reporting features
Pricing
Fivetran charges are based on monthly active rows (MAR), which count how many rows are added, updated, or deleted in a destination each month. The Free plan covers up to 500,000 rows and 5,000 transformation runs.
Paid tiers include Standard, Enterprise, and Business Critical, but prices are not posted publicly.
6. SAP Data Services
SAP Data Services (SAP BODS) is for ETL projects that need to combine and standardize records from many systems.
SAP Business Technology hosts SAP BODS, which functions effectively for companies using other SAP software. However, it still requires connections to external databases or cloud applications.
As it handles both structured and unstructured content, it can be useful for analytics, reporting, and regulatory needs. It also includes data connectors that link to SAP applications as well as third-party systems.
You can build data flows that cover extracting data, transforming it into consistent data formats, and then loading it into SAP HANA or another target system.
Beyond basic ETL, SAP BODS supports intelligent data integration through profiling, cleansing, and validation steps. These features maintain consistent standards while ensuring data integrity across different systems.
You can further do batch processing for scheduled jobs and real-time handling for situations where timing matters. For many enterprises, it doubles as both an integration layer and a full data quality management solution.
Key Features
- Universal connectivity - Connects to SAP and third-party systems, including databases, big data platforms, and flat files.
- ETL and ELT support - Handles classic extract, transform, and load jobs, or pushes logic into the database for better performance.
- Batch and real-time options - Runs large scheduled jobs or reacts instantly to new events.
- Data profiling - Scans records to flag structural or content issues before use.
- Data cleansing - Fixes, standardizes, and matches records to improve quality.
- Governance tools - Central repository for rules, lineage, and metadata tracking.
- Unstructured content handling - Pulls insights from text files, emails, or social data.
- Performance scaling - Supports parallel work and grid setups for high-volume loads.
- Integration with SAP ecosystem - Links with SAP BW, HANA, and MDG for master data and governance work.
Pros
- Native connectivity with SAP ERP, BW, and HANA
- Built-in profiling, cleansing, and validation for quality
- Can process unstructured data for deeper insight
- Centralized governance with lineage and metadata
Cons
- Steep learning curve and need for technical expertise
- Limited real-time capability compared to newer tools
- Requires heavy hardware for massive workloads
- The on-premise model feels outdated compared to modern cloud platforms
Pricing
SAP doesn’t publish prices for Data Services.
7. Informatica
Informatica is a comprehensive data integration platform since it covers integration, quality checks, master data, and controls in one stack. It works across on-prem servers and cloud services, so it fits teams that live in mixed setups.
The platform handles high data volume without falling over, which matters when daily loads reach billions of rows or when jobs run nonstop.
Informatica also places a strong focus on data quality and governance, so you can track lineage, control access, and catch issues before reports go out.
Companies pick Informatica when their data integration needs go beyond a simple sync.
Key Features
- Connectivity and connectors - Links to hundreds of databases, SaaS apps, files, APIs, and cloud systems, so teams don’t build custom links every time.
- Data transformation - Let teams clean, join, filter, sort, and reshape records through visual design or code when needed.
- Scalability and performance - Runs large jobs through parallel loads and smart partitioning to keep pipelines fast as usage grows.
- Batch and real-time runs - Supports scheduled jobs and near real-time syncs through CDC, where low delay matters.
- Data quality and governance tools - Profiles records, flags errors, applies rules, and tracks lineage with access control.
- Automation and orchestration - Schedules pipelines, chains tasks, and reduces manual upkeep, with AI help for mapping and checks.
- Monitoring and alerts - Gives logs, health views, and warnings so teams spot failures early.
- Deployment options - Runs on-prem, in the cloud, or in hybrid setups without changing the build style.
Pros
- Covers integration, quality, and governance in one stack
- Deep support for major cloud providers and warehouses
- Handles very large workloads reliably
- Detailed lineage and compliance controls
Cons
- Takes time to learn and set up properly
- Some cloud features lag behind older on-prem versions
- Support quality varies across users
- Interface can feel heavy for simple jobs
Pricing
Informatica doesn’t publicly disclose its pricing.
8. Qlik Talend
Qlik Talend brings Talend’s old open-source DNA into a bigger, enterprise-ready package under Qlik. With it, you can pull records from lots of apps, clean them up, and load them into places like cloud warehouses or lakes.
The Studio lets engineers build jobs with drag-and-drop blocks, then the system generates Java code behind the scenes. That mix of visual work and real code output makes it a versatile data integration platform.
In addition, Talend fits both ETL and ELT flows, so you can shape data before loading or push it to the target first and transform it there. Many teams lean on it for basic data integration tasks when they start, then add more complex jobs later.
Built-in checks further help keep data consistency across pipelines, which matters when sales, finance, and product teams all rely on the same dashboards.
Key Features
- Visual job design - Lets users build pipelines through a drag-and-drop Studio, then generates optimized Java for runtime.
- Data transformation - Supports joins, filters, lookups, enrichment, and reshaping with both visual steps and custom code.
- Orchestration and scheduling - Runs jobs on schedules or event triggers and chains tasks into full workflows.
- Data validation - Profiles records, flags missing or broken fields, and catches duplicates before data lands in targets.
- Real-time and CDC options - Supports streaming and change capture for low-latency needs.
- Governance and lineage - Tracks where data came from, where it went, and who changed what.
Pros
- Open-source roots give engineers deep custom control
- Visual Studio speeds up pipeline building
- Java code generation keeps the runtime flexible
- Works in cloud, on-prem, or mixed setups
Cons
- Java tuning can get messy with big jobs
- Paid features jump in price compared to the free Studio
- Studio UI feels dated and can run slowly
- Scaling very large workloads may take extra tuning
Pricing
Qlik Talend doesn’t disclose its pricing publicly.
Sync Data Across Your Revenue Stack With Activepieces
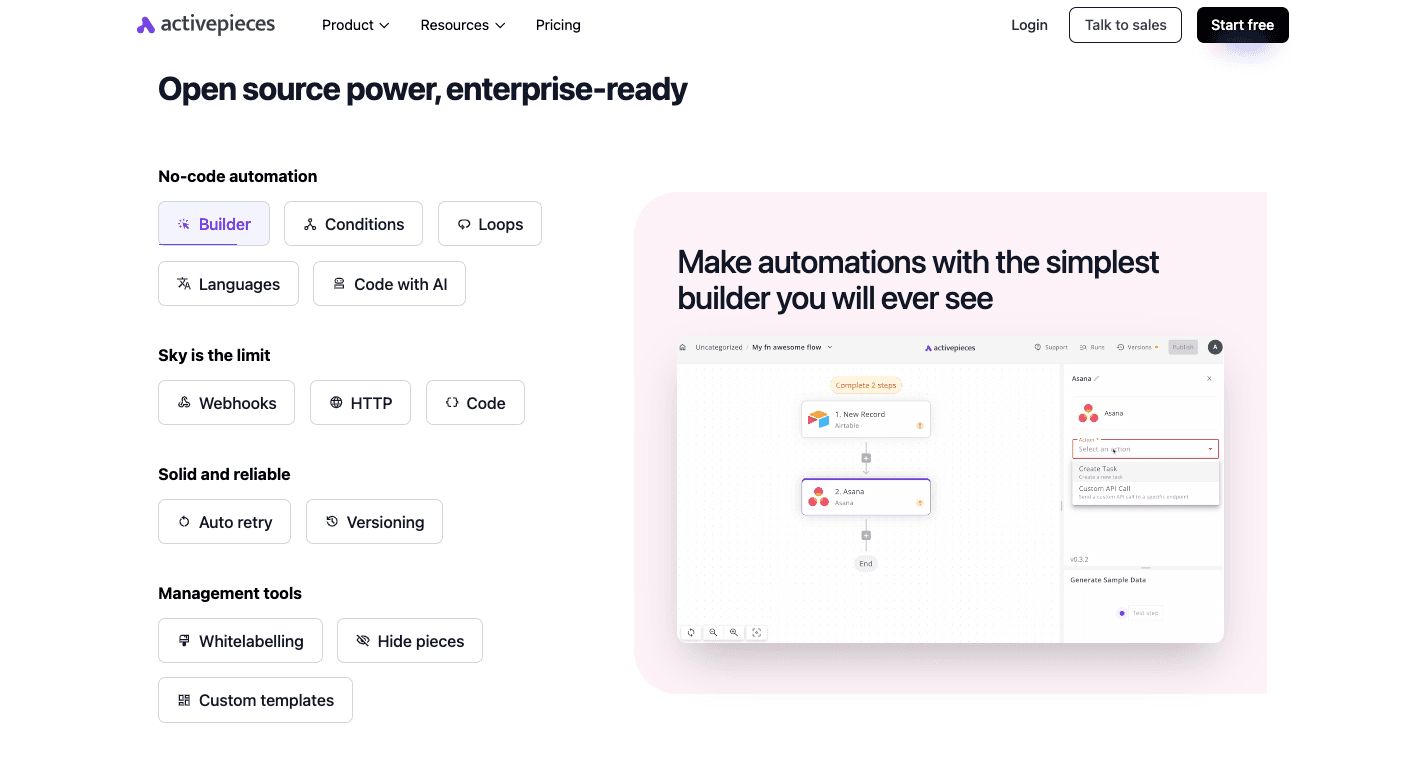
Through Activepieces, you can drag and drop pieces to build flows, while developers get full freedom with TypeScript to create custom logic. That mix means businesses don’t need separate tools for different skill levels.
The open ecosystem keeps growing fast. Every piece is open source and published on npm, with more than half contributed by the community.
You can drop in an AI agent to write, summarize, or analyze inside a workflow without leaving the builder as well. Copilot guides you while you build, so automations take minutes instead of hours.
For companies that demand full control, the self-hosted option provides network isolation and keeps sensitive data within your environment.
With Activepieces’ powerful data integration capabilities, developer-level customization, and enterprise readiness, many businesses use it to create data integration workflows.
FAQs About Data Integration Tools
What is a data integration tool?
A data integration tool pulls information from different places, organizes it, and moves it into one location so you can run reports or feed other systems. It supports data integration processes that help you combine records, improve data loading, handle structured data, and automate business processes.
Is data integration the same as ETL?
Data integration is the broader practice of joining information from many sources, while ETL is one method inside that practice. ETL focuses on extracting, transforming, and loading data from disparate systems into a centralized data repository.
Which is the best data integration tool?
The best option depends on your needs. Activepieces works well for teams that want speed, AI support, and easy automation. Enterprise teams often choose tools like Informatica or Qlik Talend. Cloud-focused groups may prefer Fivetran or Airbyte.
What are ETL and ETL tools?
ETL (Extract, Transform, Load) refers to a process that extracts data, transforms it into the right format, and loads it into a target system. ETL tools handle this workflow by connecting to sources, cleaning or reshaping the records, and completing the final load step.


